There are many situations in industry where we hear about potentially explosive atmospheres, or their abbreviated name: ATEX. It is common for these words to cause some concern, or even fear, but let's see what we can learn about explosive atmospheres to eliminate these fears.
Potentially explosive atmospheres are those where, due to the presence of a flammable substance, the favourable conditions are created for a fire to start, which could lead to a deflagration. The situations that can trigger this risk are those where two of the three elements for combustion come together:

The risk lies in the possibility that at some point, the third element could appear and ignite a fire, which could result in an explosion.
In this regard, legislation related to occupational risk prevention to protect workers health includes several references to preventing explosions, under the ATEX 2014/34/EU directive. As with other regulations concerning the safety and health of workers, the employer is ultimately responsible for ensuring safety, whether by preventing the formation of potentially explosive atmospheres, reducing their extent as much as possible, or, as a last resort, mitigating the possible consequences of an explosion and classifying each danger zone according to its risk. Through this classification, appropriate measures can be implemented in each hazardous area to prevent explosions.
“Legislation related to occupational risk prevention to protect workers health includes several references to preventing explosions, under the ATEX 2014/34/EU directive”
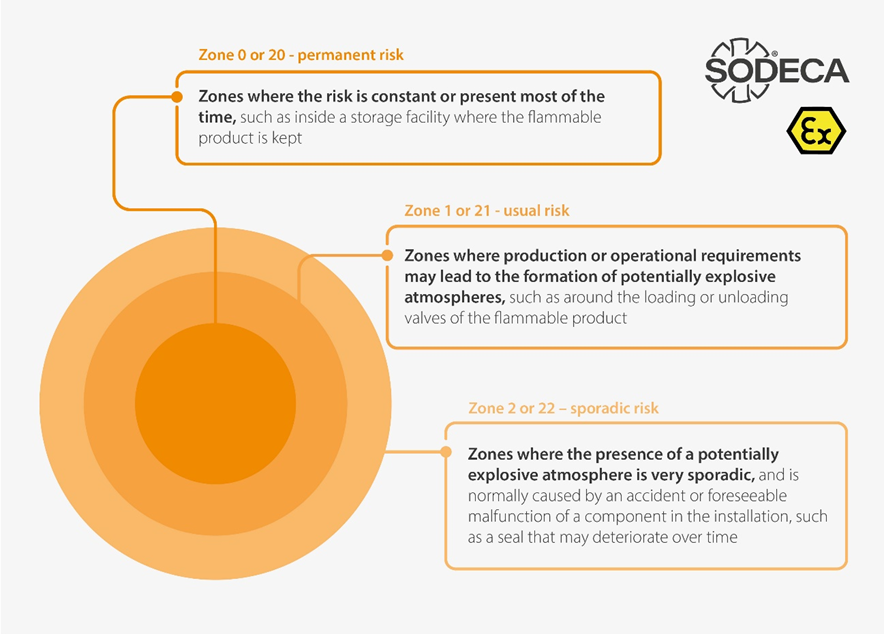
To define these risk areas, one must follow the likelihood of a potentially explosive atmosphere forming. Thus, we distinguish between areas where the risk is constant or almost always present, such as inside a tank storing the flammable product; areas where operational or production needs may trigger the presence of potentially explosive atmospheres, such as around the loading or unloading valves of the flammable product; and areas where the presence of a potentially explosive atmosphere is very sporadic, usually caused by an accident or foreseeable malfunction of some component of the installation, such as a seal that may deteriorate over time.
In any scenario, whether it is possible to avoid potentially explosive atmospheres or if the aim is to reduce their extent, ventilation can play a crucial role, especially when dealing with gaseous or liquid flammable products. To properly design the ventilation system, it is essential to know the leakage rate of the flammable product. This way, the necessary airflow can be determined to ensure ventilation that keeps the product concentration below its lower flammability limit (LFL). Similarly, when it is not possible to maintain the concentration below the LFL, an appropriate ventilation system will accelerate the dilution of the product, reducing the persistence and extent of the potentially explosive atmosphere.
In this case, when it is not possible to eliminate the risk areas, it will be necessary for the equipment installed within these areas to be protected for use in potentially explosive atmospheres.

The EN 14986:2017 standard provides guidance on how fans should be designed and manufactured to operate within ATEX zones, or to transport flammable dust or gas capable of forming a potentially explosive atmosphere inside or around the fan. It is very important to know the classification of the zone within or around the fan to select the appropriate fan with the necessary protection for operating in that space.
SODECA is a fan manufacturing company with extensive experience in designing and manufacturing ventilation solutions for use in ATEX zones, offering a wide range of industrial fans to meet the needs of companies' production processes.
